
Cloud computing is today's most trending technology as it offers opportunities for organisations to rethink and repurpose their information, technology, and services. With newer service offerings using cloud environments, companies are replacing on-premise IT solutions in exchange for IT infrastructures, platforms, and software as a service.
Cloud-based service models have gained increasing popularity as it offers tremendous flexibility and scalability. Cloud “as a service” is categorised based on the business model, application, and billing. Software as a Service (SaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) - each cloud service model addresses different user and business requirements and offers varying levels of control, security, and scalability.
SaaS, along with PaaS and IaaS, is the most widely applied cloud service. Generally, cloud computing solutions are offered as subscription-based services.
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Software as a Service (SaaS) is a web-based software deployment model that allows users to access the software via a web browser. Software is hosted in the cloud and is accessed through the internet meaning you don't have to pay for servers or software with SaaS. Software maintenance is taken care of by the service provider, and you simply connect to the SaaS application via a console dashboard or Application Programming Interface (API). The user can access the application whenever they want rather than keeping the software on their computer, hence it is referred to as on-demand software. These applications run on the cloud and do not require a download to a local device.
The SaaS model offers benefits that can boost an organisation's productivity and flexibility. For example, the SaaS provider manages the software and hardware, software upgrades, and data, which reduces the need for internal IT staff.
Examples of SaaS include Zoho, Salesforce, Gmail, Google Drive, and Microsoft Office 365.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Platform as a service (PaaS) is a computing model in which a third-party provider hosts a computing platform that allows users to develop their applications. In other words, PaaS provides a framework for application creation and deployment. The technical stack required for application development is available in the cloud, so there is no need for a download or a local installation. Developers can focus on building their applications without worrying about operating systems, software updates, storage, or infrastructure. This allows the service provider to handle all the necessary infrastructures.
PaaS enables developers to create applications without worrying about underlying infrastructure or operating systems. The database and language are abstracted away, allowing the developer to concentrate on the application design while the platform handles the database and language. PaaS service models are easily adaptable to the needs of developers.
Examples of PaaS include AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Heroku, Google App Engine, OpenShift, Apache Stratos, and Flynn.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is a cloud computing service model that provides a platform for a client's infrastructure needs. This includes servers, operating systems, applications, storage, and network equipment. Furthermore, IaaS allows you to outsource all or a portion of your infrastructure to a third-party service provider. The service provider manages the hardware, software, and network infrastructure elements. IaaS allows you to purchase only the computing you require and scale it up or down as needed. If you want to migrate an application from an on-premise data centre to the cloud, choose an IaaS model. You will be able to continue with the migration with a few changes.
IaaS is advantageous when scalability and quick provisioning are pivotal. Specifically, IaaS allows you to quickly create multiple virtual machines and pay only for the resources you use. It is primarily designed for small businesses that lack the resources to manage their servers and are also required to assist larger organisations.
Examples of IaaS: Microsoft Azure, Stackscale, Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, and VMware.
The graphical representation below shows how the three models compare in terms of who manages what.
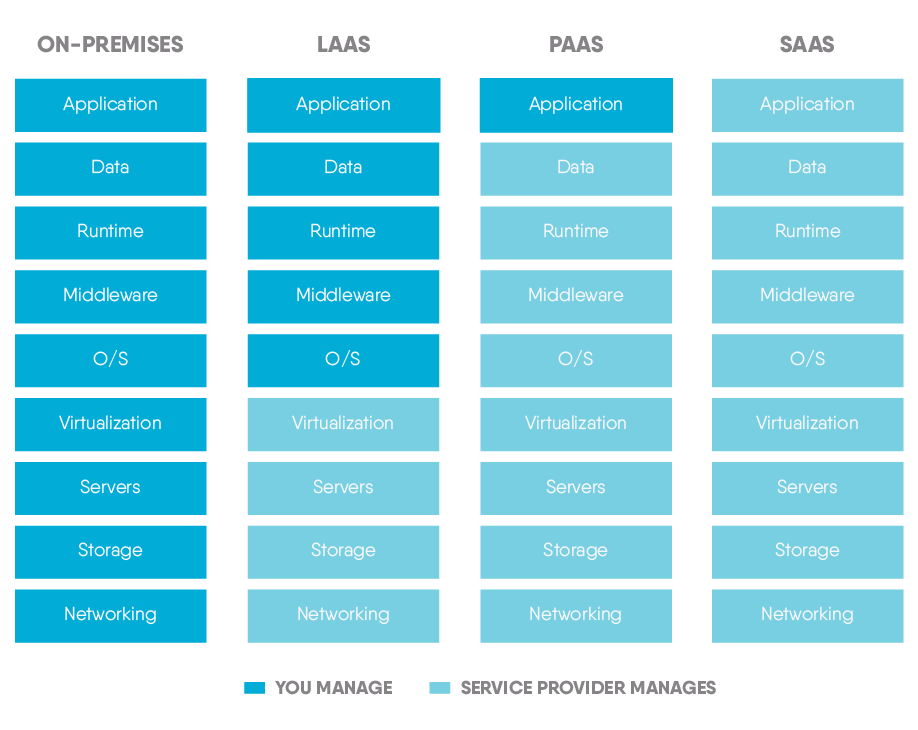
To summarise, the IaaS model provides the computing resources that businesses require to host, build, and run their services. The PaaS paradigm provides a development and deployment environment for developers, whilst the SaaS model delivers software to users and businesses via the internet.
Getting started with cloud services, integrating them with your application, choosing the right service and delivery model can be overwhelming. You need to look at the security, functionality, and cost features when you want to start with a Cloud “as a service”.
At BTC, our team of experts helps you study the business case, identify the areas of improvement, and help you choose the right model that fits your requirement. Get in touch with our team today to begin your cloud computing journey by emailing us on [email protected].